|
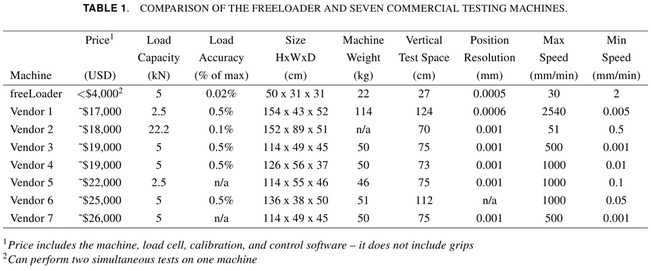
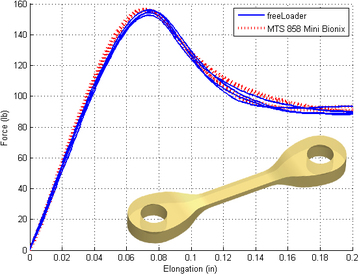
The FreeLoader is a low cost, desktop size, open source, universal testing machine, designed for inexpensive high-throughput material testing. A freeLoader can apply tensile and compression loads of 5 kN with +/- 1.8 N accuracy, and at rates ranging from 2 mm/min to 30 mm/min. Each freeLoader can perform two simultaneous tests and costs under US$4,000. Information on the freeLoader was first published at the 2011 ASME IDETC/CIE Mechanisms and Robotics Conference. A link to this paper can be found below. This page contains information that suplements the original paper including a user manual with specific build instructions, downloadable control software and source code, and links useful websites. For those interested in learning more about the freeLoader or building freeLoaders of their own, it is recommended that you first read the ASME paper to get a better idea of the capabilities, intended uses, and goals for this machine. Next you should read through the user manual and FAQ from this webiste for a more complete picture of what it takes to build and use a freeLoader (it's not too hard at all). Note: We suggest replacing the RX motors in the original design with the new Dynamixel MX-64R motors.They have encoders with twice the resolution and no dead zone, so the speed control is much better. |
learn more |
ASME Paper
Feeloader User Manual SolidWorks 2008 Files (see also Parasolid files and laser cutting file for plates) Control software executable (See source code and MATLAB Converter) New: PyLoader Python library and tutorial. (Thanks to Anthony McNicoll) |
Project participants |
|
Related Publications |
|